 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
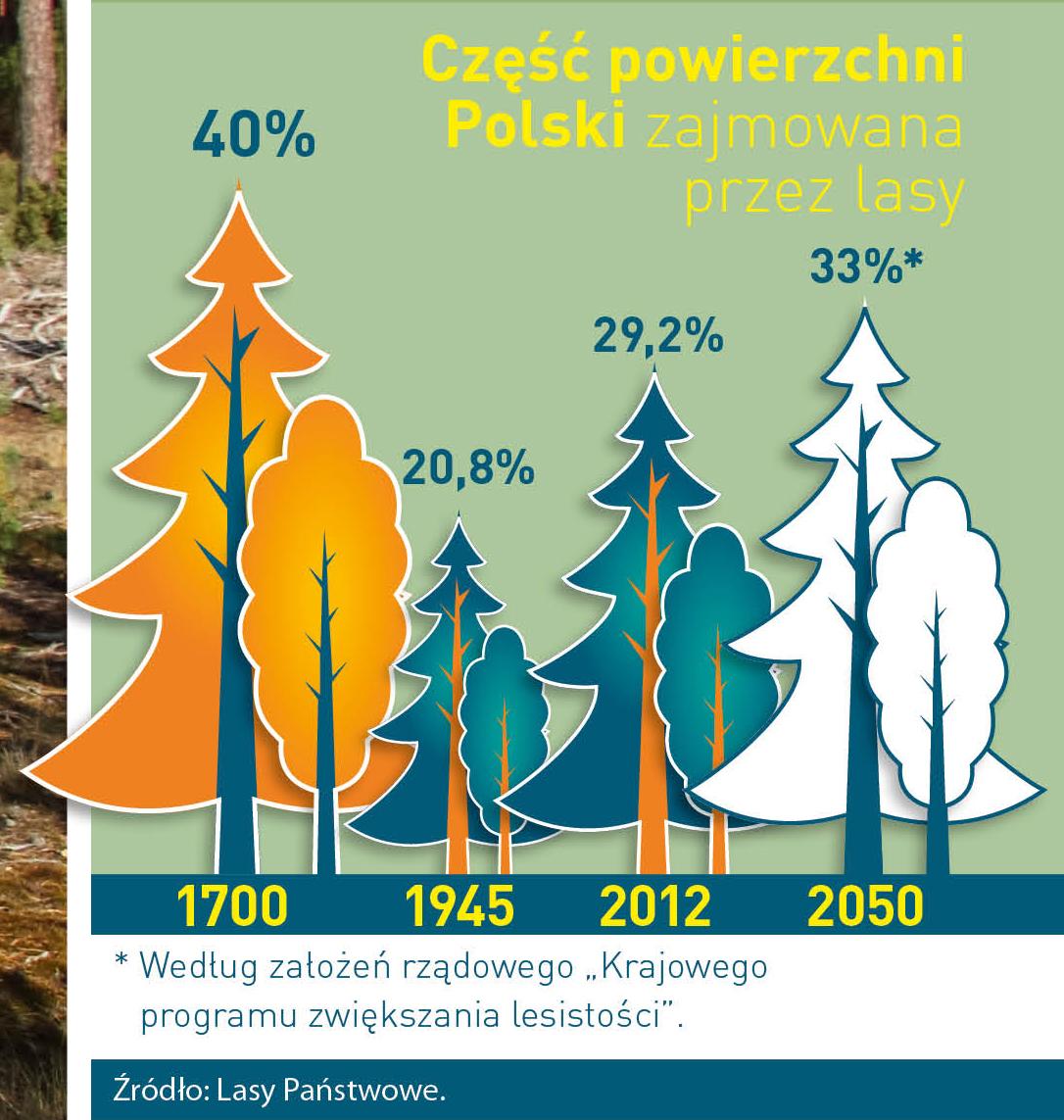
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Potwierdziły się nasze obserwacje - TO SZAKAL ZŁOCISTY (Canis aureus)!
Potwierdziły się nasze obserwacje - TO SZAKAL ZŁOCISTY (Canis aureus)!
Nadleśnictwo Kwidzyn otrzymało w przedostatni dzień starego roku, czyli 30 grudnia 2016 r. około godziny 14:00 informację, że na terenie leśnictwa Wilki (nieopodal miejscowości Węgry) zauważono „dziwnego lisa”, ewentualnie „małego wilka”.
Na miejsce udał się pracownik Nadleśnictwa – Andrzej Bołkowski, który na pierwszy rzut oka stwierdził, że jest to szakal. Cechą charakterystyczną tego gatunku jest zrośnięcie opuszków środkowych palców przednich łap. Nie miał jednak 100% pewności, ponieważ nigdy nie widział z bliska tego gatunku. Zwierzę było martwe i nosiło znaki walki z innymi drapieżnikami.
O zdarzeniu poinformowaliśmy właściwą RDLP i RDOŚ oraz Powiatowego lekarza weterynarii. Ze względu na to, że jest to swoista osobliwość przyrodnicza, przesłaliśmy również informację do Instytutu Badania Ssaków PAN w Białowieży. Pracownicy Instytutu na podstawie zdjęć stwierdzili, że jest to szakal złocisty, choć należy to jeszcze potwierdzić. Zwierzę wzbudziło duże zainteresowanie innych instytucji. W poniedziałek, kiedy informacja trafiła do IBS-u PAN z prośbą o próbki tkanki i sierści odezwały się także: Uniwersytet Warszawski, Wydział Genetyki i Biotechnologii oraz Stowarzyszenie dla natury „Wilk".
We wtorek rano po szakala zjawił się pracownik Instytutu Badania Ssaków PAN z Białowieży. Czekaliśmy na potwierdzenie gatunku z dużą ciekawością. W środę dostaliśmy informację, iż ze 100% pewnością to szakal złocisty. Poinformował nas o tym Rafał Kowalczyk – Dyrektor IBS-u PAN. Nasze obserwacje potwierdziły się!
Znalezione zwierzę okazało się być 3-4 letnim samcem, o wadze ok. 14 kg. Według oceny pracowników Instytutu zwierzę było całe pogryzione, więc przypuszczalnie przed śmiercią stoczyło walkę z innym drapieżnikiem. Na terenie, gdzie został znaleziony szakal od pewnego czasu obserwujemy bytność 2 wilków, więc mogą być to domniemani sprawcy śmierci szakala złocistego.
Jak podaje IBS nie było możliwości preparacji zwierzęcia, ze względu na to, że leżało w lesie ok. 2 tygodni. Zachowany zostanie jednak szkielet znaleziska. Dalsze badania pozwolą także określić dietę drapieżnika i dostarczą o nim wielu ciekawych informacji, np. skąd przywędrował nasz gość.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański



 Źródło: Wikipedia / Lee R.Berger
Źródło: Wikipedia / Lee R.Berger
 fot. Andrzej Bołkowski
fot. Andrzej Bołkowski
 fot. Andrzej Bołkowski
fot. Andrzej Bołkowski